General Mathematics Objective 2024 Cover
Answer all the questions.
Mathematical tables may be used in any question. The use of non-programmable, silent and cordless calculator is allowed.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct option for each question and shade in pencil , on your answer sheet, the answer space which bears the same letter as the option you have chosen.
Give only one answer to each question. An example is given below.
The ages, in years, of four boys are 10, 12, 14 and 18. What is the average age of the boys?
A. 12 years B. \( 12\frac{1}{2} \) years C. 13 years D. \( 13\frac{1}{2} \) years
The correct answer is \( 13\frac{1}{2} \) years, which is lettered D , and therefore answer space D would be shaded.
Think carefully before you shade the answer spaces; erase completely any answers you wish to change.
1. R, S, and T are subsets of the universal set \( U = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\} \) such that \( R = \{1, 2, 3\} \), \( S = \{2, 3, 4\} \), and \( T = \{4, 5\} \). Find \( (R \cup S) \cap T' \).
A. \(\{4\}\)B. \(\{1, 2, 3\}\)C. \(\{4, 5\}\)D. \(\{1, 2, 3, 4\}\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
We are given:
Universal set \( U = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\} \)
Subset \( R = \{1, 2, 3\} \)
Subset \( S = \{2, 3, 4\} \)
Subset \( T = \{4, 5\} \)
Step 1: Find \( R \cup S \)
\[
R \cup S = \{1, 2, 3\} \cup \{2, 3, 4\}\] \[= \{1, 2, 3, 4\}
\]
Step 2: Find \( T' \) (complement of \( T \) in the universal set)
\[
T' = U - T\] \[= \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\} - \{4, 5\}\] \[= \{1, 2, 3\}
\]
Step 3: Find \( (R \cup S) \cap T' \)
\[
(R \cup S) \cap T'\] \[= \{1, 2, 3, 4\} \cap \{1, 2, 3\}\] \[= \{1, 2, 3\}
\]
Final Answer: \( B. \{1, 2, 3\} \)
2. Given \(234_x = 76_9\), find the value of \(x\).
A. 5B. 6C. 7D. 8
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Convert \(76_9\) to decimal (base 10)
\[
76_9
= 7 \times 9^1 + 6 \times 9^0\]
\[= 7 \times 9 + 6 \times 1\]
\[= 63 + 6
= 69
\]
Step 2: Express \(234_x\) in decimal form
\[
234_x
= 2 \times x^2 + 3 \times x^1 + 4 \times x^0\]
\[= 2x^2 + 3x + 4
\]
Step 3: Set up the equation
\[
2x^2 + 3x + 4 = 69
\]
Step 4: Rearrange the equation
\[
2x^2 + 3x + 4 - 69 = 0\]
\[= 2x^2 + 3x - 65 = 0
\]
Step 5: Solve using the quadratic formula
\[
x = \frac{-3 \pm \sqrt{3^2 - 4 \cdot 2 \cdot (-65)}}{2 \cdot 2}\]
\[= \frac{-3 \pm \sqrt{9 + 520}}{4}\]
\[= \frac{-3 \pm \sqrt{529}}{4}\]
\[= \frac{-3 \pm 23}{4}
\]
Step 6: Evaluate the two possible values
\[
x = \frac{-3 + 23}{4} = \frac{20}{4} = 5
\]
\[
x = \frac{-3 - 23}{4}\] \[= \frac{-26}{4} = -6.5 \quad (\text{not valid})
\]
Final Answer: \( A. \ 5 \)
3. Express the difference between \( \frac{5}{6} \) and \( \frac{1}{3} \) as a percentage.
A. 30%B. 40%C. 50%D. 60%
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Find the difference between \( \frac{5}{6} \) and \( \frac{1}{3} \)
\[
\frac{5}{6} - \frac{1}{3}
= \frac{5}{6} - \frac{2}{6}
= \frac{3}{6}
= \frac{1}{2}
\]
Step 2: Convert \( \frac{1}{2} \) to a percentage
\[
\frac{1}{2} = 0.5 = 0.5 \times 100 = 50\%
\]
Final Answer: \( C. \ 50\% \)
4. Given that \( \log_x 64 = 3 \), find the value of \( x \).
A. 1B. 3C. 4D. 5
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Use the definition of logarithms
\[
\log_x 64 = 3 \Rightarrow x^3 = 64
\]
Step 2: Solve for \( x \)
\[
x = \sqrt[3]{64}
\]
Step 3: Checking small integers:
If \( x = 2 \), then \( 2^3 = 8 \)
If \( x = 3 \), then \( 3^3 = 27 \)
If \( x = 4 \), then \( 4^3 = 64 \)
Final Answer: \( C. \ 4 \)
5. Write 20,900 in standard form.
A. \(2.09 \times 10^{-4}\)B. \(2.1 \times 10^{-4}\)C. \(2.1 \times 10^{4}\)D. \(2.09 \times 10^{4}\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Identify the number
The number is \(20,900\)
Step 2: Place the decimal point
Write it as \(20,900.0\)
Step 3: Move the decimal point until only one non-zero digit is in front of it
Move 4 places to the left:
\(20,900.0 \to 2.0900\)
Step 4: Since we moved the decimal point 4 places to the left, the exponent is \(+4\)
Step 5: Write the number in standard form
\(2.09 \times 10^{4}\)
Final Answer: \(D.\ 2.09 \times 10^{4}\).
6. Find the fifth term of the sequence \(14, 18, 22, \ldots\)
A. 20B. 30C. 34D. 48
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Identify the first term \(a_1\)
\(a_1 = 14\)
Step 2: Subtract the first term from the second term \(d\)
\(d = 18 - 14 = 4\)
Step 3: Use the formula for the \(n^\text{th}\) term of an arithmetic sequence:
\[
a_n = a_1 + (n - 1)d
\]
Step 4: Find the 5th term \(a_5\)
\[
a_5 = 14 + (5 - 1) \times 4\] \[= 14 + 16 = 30
\]
Final answer B. \(30\)
7. Find the percentage error in approximating 3.75 cm to be 4.0 cm.
A. \(6.67\%\)B. \(6.25\%\)C. \(0.25\%\)D. \(25\%\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Use the percentage error formula:
\[
\text{Percentage Error} = \left( \frac{\left| \text{Approximate Value} - \text{Actual Value} \right|}{\text{Actual Value}} \right) \times 100
\]
Step 2: Substitute the given values:
\[
\text{Percentage Error} = \left( \frac{\left| 4.0 - 3.75 \right|}{3.75} \right) \times 100
\]
Step 3: Perform the calculations:
\[
= \left( \frac{0.25}{3.75} \right) \times 100
\]
\[
= 6.67\%
\]
Final Answer: \(A.\ 6.67\%\).
8. Solve: \(3x^2 + 4x = 4\).
A. \(x = 2, \frac{2}{3}\)B. \(x = 2, -\frac{2}{3}\)C. \(x = -2, \frac{2}{3}\)D. \(x = -2, -\frac{2}{3}\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Rewrite the equation in standard form:
\(3x^2 + 4x - 4 = 0\)
Step 2: Use the quadratic formula:
\[
x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}
\]
Step 3: Substitute the values \(a = 3\), \(b = 4\), \(c = -4\):
\[
x = \frac{-4 \pm \sqrt{16 + 48}}{6}
\]
Step 4: Solve:
\[
x = \frac{-4 \pm 8}{6}
\]
\[
x = \frac{4}{6} = \frac{2}{3} \quad \text{or}\] \[\quad x = \frac{-12}{6} = -2
\]
Final Answer: \(C.\ x = -2, \frac{2}{3}\).
9. Given that \(5 - \frac{1}{2}x \leq 7\), where \(x\) is real, find \(x\).
A. \(x \leq -4\)B. \(x \geq -4\)C. \(x \geq 4\)D. \(x \leq -1\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Isolate the term with \(x\):
\[
5 - \frac{1}{2}x \leq 7
\]
Subtract 5 from both sides:
\[
-\frac{1}{2}x \leq 2
\]
Step 2: Multiply by \(-2\) and reverse the inequality:
\[
x \geq -4
\]
Final Answer: \(B.\ x \geq -4\).
10. A variable \(P\) varies directly as the cube root of \(Q\). If \(P = 4\) when \(Q = 8\), find \(P\) when \(Q = 64\).
A. 16B. 8C. 4D. 2
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Use the variation relationship
\(P \propto \sqrt[3]{Q}\), so \(P = k\sqrt[3]{Q}\), where \(k\) is a constant
Step 2: Find the constant \(k\) using the values \(P = 4\) and \(Q = 8\)
\[
4 = k\sqrt[3]{8} = k \times 2 \Rightarrow k = 2
\]
Step 3: Use the equation to find \(P\) when \(Q = 64\)
\[
P = 2 \times \sqrt[3]{64} = 2 \times 4 = 8
\]
Final Answer: \(B. \ 8\)
11. Make \( r \) the subject of the relation \( \frac{1}{p} = q - \frac{1}{r} \).
A. \( r = \frac{p}{q - p} \)B. \( r = \frac{p}{q(p - 1)} \)C. \( r = \frac{p}{qp - 1} \)D. \( r = \frac{q}{q(p - 1)} \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Rearrange the equation to isolate \( \frac{1}{r} \).
\[
\frac{1}{p} = q - \frac{1}{r}
\]
Add \( \frac{1}{r} \) to both sides:
\[
\frac{1}{p} + \frac{1}{r} = q
\]
Subtract \( \frac{1}{p} \) from both sides to get:
\[
\frac{1}{r} = q - \frac{1}{p}
\]
Step 2: Express the right-hand side with a common denominator.
The term \( \frac{1}{p} \) has a denominator of \( p \), so rewrite \( q \) as \( \frac{qp}{p} \):
\[
\frac{1}{r} = \frac{qp}{p} - \frac{1}{p}
\]
Since both terms have the denominator \( p \), subtract:
\[
\frac{1}{r} = \frac{qp - 1}{p}
\]
Step 3: Solve for \( r \) by inverting the fraction.
\[
r = \frac{p}{qp - 1}
\]
Final Answer: \( C.\ r = \frac{p}{qp - 1} \).
12. For what value of \( R \) is \( 3x^2 - 7x + R \) a perfect square?
A. \( 8 \frac{1}{6} \)B. \( 4 \frac{1}{12} \)C. \( 2 \frac{1}{24} \)D. \( 1 \frac{13}{36} \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Express the quadratic function as a perfect square.
Since \( 3x^2 - 7x + R \) must be in the form \( (ax + b)^2 \), we expand:
\[
(ax + b)^2 = a^2x^2 + 2abx + b^2
\]
Comparing coefficients, we set:
\[
a^2 = 3, \quad 2ab = -7, \quad b^2 = R
\]
Step 2: Solve for \( a \).
\[
a = \sqrt{3}
\]
Step 3: Solve for \( b \).
\[
2(\sqrt{3})b = -7\]
\[b = \frac{-7}{2\sqrt{3}} \cdot
\]
Simplify The Fraction:
\[
\frac{-7}{2\sqrt{3}} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{-7\sqrt{3}}{2 \cdot 3} = \frac{-7\sqrt{3}}{6}
\]
Step 4: Solve for \( R \).
\[
R = b^2 = \left(\frac{-7\sqrt{3}}{6}\right)^2
\]
\[
R = \frac{49 \times 3}{36} = \frac{147}{36} = 4 \frac{1}{12}
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ 4 \frac{1}{12} \).
13. A total of 222 books were shared among 7 students and 5 teachers. If each student received 6 books less than a teacher, find the number of books each student received.
A. \( 28 \)B. \( 18 \)C. \( 16 \)D. \( 12 \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Define variables.
Let \( x \) be the number of books each student received.
Since each student received 6 books less than a teacher, teachers received \( x + 6 \) books each.
Step 2: Form the equation.
Total number of books distributed:
\[
7x + 5(x + 6) = 222
\]
Step 3: Expand and simplify.
\[
7x + 5x + 30 = 222
\]
\[
12x + 30 = 222
\]
Step 4: Solve for \( x \).
\[
12x = 222 - 30
\]
\[
12x = 192
\]
\[
x = \frac{192}{12} = 16
\]
Final Answer: \( C.\ 16 \).
14. A solid cone is 7 cm high and the base radius is 1.5 cm. Calculate the volume of the cone. [Take \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)]
A. 49.5 cm\(^3\)B. 33.0 cm\(^3\)C. 16.5 cm\(^3\)D. 11.0 cm\(^3\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Recall the formula for the volume of a cone
\[
V = \frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h
\]
Step 2: Substitute the given values \(r = 1.5 \, \text{cm}\), \(h = 7 \, \text{cm}\), \(\pi = \frac{22}{7}\)
\[
V = \frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times (1.5)^2 \times 7
\]
Step 3: Simplify the expression
\[
V = \frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 2.25 \times 7
\]
\[
V = \frac{1}{3} \times 22 \times 2.25
\]
\[
V = \frac{1}{3} \times 49.5 = 16.5 \, \text{cm}^3
\]
Final Answer: \(C. \ 16.5 \, \text{cm}^3\)
15. Simplify: \( \frac{6x - 1}{4} - \frac{3 - 2x}{6} + 2 \).
A. \( \frac{22x + 15}{12} \)B. \( \frac{22x + 17}{12} \)C. \( \frac{22x - 15}{12} \)D. \( \frac{22x - 17}{12} \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Find the common denominator.
Denominators 4 and 6 have the least common denominator of 12, so rewrite:
\[
\frac{3(6x - 1)}{12} - \frac{2(3 - 2x)}{12} + 2
\]
Step 2: Expand the fractions.
\[
\frac{18x - 3}{12} - \frac{6 - 4x}{12} + 2
\]
Step 3: Combine like terms.
\[
\frac{18x - 3 - 6 + 4x}{12} + 2
\]
\[
\frac{22x - 9}{12} + 2
\]
Step 4: Convert 2 into a fraction.
\[
2 = \frac{24}{12}
\]
Step 5: Add fractions.
\[
\frac{22x - 9 + 24}{12}
\]
\[
\frac{22x + 15}{12}
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ \frac{22x + 15}{12} \).
16. By how much is the sum of \( 6x \), \( (12x - 10) \), and \( (18x + 2) \) less than \( 60x \)?
A. \( -24x - 8 \)B. \( -24x + 8 \)C. \( 24x - 8 \)D. \( 24x + 8 \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Compute the sum.
\[
6x + (12x - 10) + (18x + 2)
\]
Distribute and combine like terms:
\[
6x + 12x - 10 + 18x + 2\] \[= (6x + 12x + 18x) + (-10 + 2)
\]
\[
36x - 8
\]
Step 2: Find the difference from \( 60x \).
\[
(36x - 8) - 60x
\]
Distribute:
\[
36x - 8 - 60x
\]
\[
-24x - 8
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ -24x - 8 \).
17. Express \( \frac{1}{a - b} - \frac{1}{a + b} \) as a single fraction.
A. \( \frac{1}{2a} \)B. \( \frac{-1}{2b} \)C. \( \frac{2a}{a^2 - b^2} \)D. \( \frac{2b}{a^2 - b^2} \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Find a common denominator.
The denominators are \( a - b \) and \( a + b \), so their common denominator is:
\[
(a - b)(a + b) = a^2 - b^2
\]
Step 2: Rewrite the fractions.
\[
\frac{1}{a - b} - \frac{1}{a + b}\] \[= \frac{(a + b) - (a - b)}{a^2 - b^2}
\]
Step 3: Simplify the numerator.
\[
a + b - a + b = 2b
\]
Step 4: Write the final fraction.
\[
\frac{2b}{a^2 - b^2}
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ \frac{2b}{a^2 - b^2} \).
18. A ladder, 9 m long leans against a vertical wall making an angle of \(64^\circ\) with the horizontal. Calculate, correct to one decimal place, the distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall.
A. \(8.1 \text{ m}\)B. \(18.5 \text{ m}\)C. \(3.9 \text{ m}\)D. \(5.8 \text{ m}\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Identify the trigonometric function.
The ladder forms a right-angled triangle with the wall. We use cosine since we need the adjacent side:
\[
\cos \theta = \frac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]
\[\cos 64^\circ = \frac{x}{9}
\]
Step 2: Solve for \( x \), the horizontal distance.
\[
x = 9 \times \cos 64^\circ
\]
Using a calculator:
\[
x = 9 \times 0.4384
\]
Step 3: Final calculation.
\[
x = 3.9 \text{ m}
\]
Final Answer: \( C.\ 3.9 \text{ m} \).
19. The interior angles of a polygon are \( x^\circ \), \( (2x)^\circ \), \( (x + 10)^\circ \), \( (x - 10)^\circ \), and \( (x + 60)^\circ \). Find the value of \( x \).
A. \( 80 \)B. \( 70 \)C. \( 60 \)D. \( 50 \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Use the sum of interior angles formula.
The sum of interior angles of a polygon is given by:
\[
\text{Sum} = (n - 2) \times 180^\circ
\]
Since the polygon has 5 sides:
\[
\text{Sum} = (5 - 2) \times 180 = 540^\circ
\]
Step 2: Form the equation.
The sum of given angles:
\[
x + 2x + (x + 10) + (x - 10) + (x + 60)
\] \[ = 540 \]
Step 3: Simplify the equation.
\[
x + 2x + x + 10 + x - 10 + x + 60 = 540
\]
\[
6x + 60 = 540
\]
Step 4: Solve for \( x \).
\[
6x = 540 - 60
\]
\[
6x = 480
\]
\[
x = \frac{480}{6} = 80
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ 80 \).
20. Find the length of the line joining the points \( M(-3, 4) \) and \( N(5, -2) \).
A. \( 5 \) unitsB. \( 6 \) unitsC. \( 10 \) unitsD. \( 12 \) units
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Use the distance formula.
\[
d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]
Substituting the given points \( M(-3, 4) \) and \( N(5, -2) \):
\[
d = \sqrt{(5 - (-3))^2 + (-2 - 4)^2}
\]
Step 2: Simplify the expressions.
\[
d = \sqrt{(5 + 3)^2 + (-2 - 4)^2}
\]
\[
d = \sqrt{(8)^2 + (-6)^2}
\]
\[
d = \sqrt{64 + 36}
\]
Step 3: Compute the final result.
\[
d = \sqrt{100} = 10
\]
Final Answer: \( C.\ 10 \) units.
21. The bearing of \( N 62^\circ W \) is the same as:
A. \( 298^\circ \)B. \( 242^\circ \)C. \( 152^\circ \)D. \( 062^\circ \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Understanding the notation.
The bearing \( N 62^\circ W \) means it is measured 62° west from north.
Step 2: Convert to true bearing.
True bearings are measured clockwise from north \( (0^\circ) \), so:
\[
360^\circ - 62^\circ = 298^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ 298^\circ \).
22. Calculate the standard deviation of \( 6, 7, 8, 9, \) and \( 10 \).
A. \( \sqrt{2} \)B. \( \sqrt{3} \)C. \( 2\sqrt{2} \)D. \( \sqrt{10} \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Calculate the mean.
\[
\mu = \frac{6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10}{5}
\]
\[
\mu = \frac{40}{5} = 8
\]
Step 2: Compute the variance.
\[
\sigma^2 = \frac{(6-8)^2 + (7-8)^2 + (8-8)^2 + (9-8)^2 + (10-8)^2}{5}
\]
\[
= \frac{(-2)^2 + (-1)^2 + 0^2 + 1^2 + 2^2}{5}
\]
\[
= \frac{4 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 4}{5}
\]
\[
= \frac{10}{5} = 2
\]
Step 3: Find the standard deviation.
\[
\sigma = \sqrt{2}
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ \sqrt{2} \).
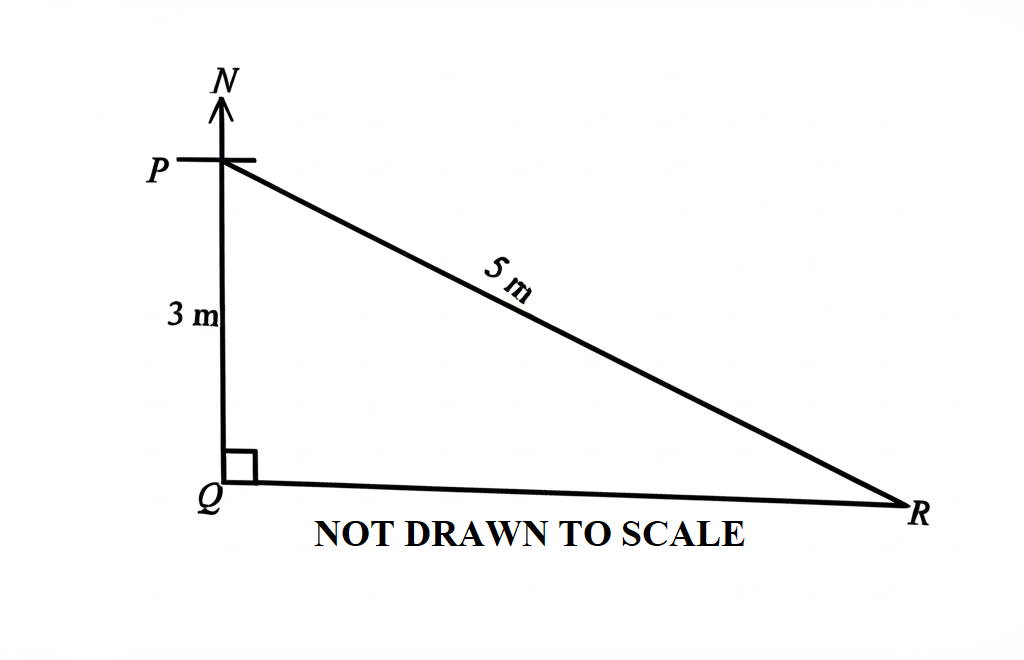
23.
In the diagram, \( |\overline{PQ}| = 3 \) m, \( |\overline{PR}| = 5 \) m, and \( \angle PQR = 90^\circ \).
Find, correct to the nearest degree, the bearing of \( P \) from \( R \).
A. \( 127^\circ \)B. \( 143^\circ \)C. \( 307^\circ \)D. \( 323^\circ \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Use trigonometry to find \( \theta \).
Since \( |\overline{PR}| \) is the hypotenuse and \( |\overline{PQ}| \) is the opposite side, we use sine:
\[
\sin \theta = \frac{|\overline{PQ}|}{|\overline{PR}|}
\]
\[
\sin \theta = \frac{3}{5}
\]
Using a calculator:
\[
\theta = \sin^{-1} (0.6) = 37^\circ
\]
Step 2: Convert to a bearing.
Bearing is measured clockwise from north \( (0^\circ) \), so:
\[
360^\circ - 37^\circ = 323^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ 323^\circ \).
24. Given that $3,750.00 amounts to $4,250.00 in 6 years, find the rate of simple interest per annum.
A. \( 2 \frac{1}{6} \% \)B. \( 2 \frac{2}{9} \% \)C. \( 3 \frac{1}{6} \% \)D. \( 3 \frac{2}{9} \% \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Use the simple interest formula.
\[
SI = \frac{P \times r \times t}{100}
\]
Where:
\( A = 4,250.00 \) (final amount)
\( P = 3,750.00 \) (principal)
\( t = 6 \) years
Step 2: Find the simple interest.
\[
SI = A - P\] \[= 4,250 - 3,750 = 500
\]
Step 3: Solve for \( r \).
\[
500 = \frac{3,750 \times r \times 6}{100}
\]
\[
500 \times 100 = 3,750 \times r \times 6
\]
\[
50,000 = 22,500r
\]
\[
r = \frac{50,000}{22,500} = \frac{50}{22.5}\] \[= \frac{20}{9} = 2 \frac{2}{9} \%
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ 2 \frac{2}{9} \% \).
25. A side of a rectangle is 7 m shorter than the adjacent side. If the perimeter of the rectangle is 46 m, find the length of the longer side.
A. \( 8 \) mB. \( 10 \) mC. \( 12 \) mD. \( 15 \) m
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Define the variables.
Let the longer side be \( x \), then the shorter side is \( x - 7 \).
Step 2: Use the perimeter formula.
\[
P = 2(\text{length} + \text{width})
\]
Given \( P = 46 \):
\[
46 = 2(x + (x - 7))
\]
Step 3: Solve for \( x \).
\[
46 = 2(2x - 7)
\]
\[
46 = 4x - 14
\]
\[
4x = 46 + 14
\]
\[
4x = 60
\]
\[
x = \frac{60}{4} = 15
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ 15 \) m.
26. Given that \( \cos 2x = \sin 28^\circ \), where \( 0^\circ < x < 90^\circ \), find the value of \( x \).
A. \( 28^\circ \)B. \( 31^\circ \)C. \( 57^\circ \)D. \( 62^\circ \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Use the identity relating sine and cosine.
Since \( \cos A = \sin (90^\circ - A) \), we rewrite:
\[
\cos 2x = \sin (90^\circ - 2x)
\]
Comparing with \( \sin 28^\circ \), we set:
\[
90^\circ - 2x = 28^\circ
\]
Step 2: Solve for \( x \).
\[
2x = 90^\circ - 28^\circ
\]
\[
2x = 62^\circ
\]
\[
x = \frac{62^\circ}{2} = 31^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ 31^\circ \).
27. A cuboid has the same volume as a cylinder. If the base radius of the cylinder is 7 cm and the base area of the cuboid is 1,232 cm², express as a ratio the height of the cuboid to the height of the cylinder.
A. \( 8:1 \) B. \( 3:1 \) C. \( 1:3 \) D. \( 1:8 \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Compute the volume of the cylinder using the formula:
\[
V = \pi r^2 h
\]
Substituting the given values:
\[
V = \frac{22}{7} \times (7)^2 \times h
\]
\[
V = \frac{22}{7} \times 49 \times h
\]
\[
V = \frac{1078}{7} \times h
\]
\[
V = 154 h
\]
Step 2: Compute the volume of the cuboid.
Since the cuboid has the same volume as the cylinder, we equate:
\[
V_{\text{cuboid}} = V_{\text{cylinder}}
\]
\[
1,232 \times H = 154h
\]
Step 3: Solve for the ratio.
\[
H : h = \frac{154h}{1232}
\]
\[
H : h = \frac{154}{1232} = \frac{1}{8}
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ 1:8 \).
28. A regular polygon has 15 sides. Calculate the size of each interior angle.
A. \( 126^\circ \)B. \( 136^\circ \)C. \( 146^\circ \)D. \( 156^\circ \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Use the interior angle formula.
\[
\text{Interior Angle} = \frac{(n - 2) \times 180^\circ}{n}
\]
Where \( n = 15 \) (number of sides):
\[
\text{Interior Angle} = \frac{(15 - 2) \times 180}{15}
\]
Step 2: Simplify the expression.
\[
= \frac{13 \times 180}{15}
\]
\[
= \frac{2340}{15}
\]
\[
= 156^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ 156^\circ \).
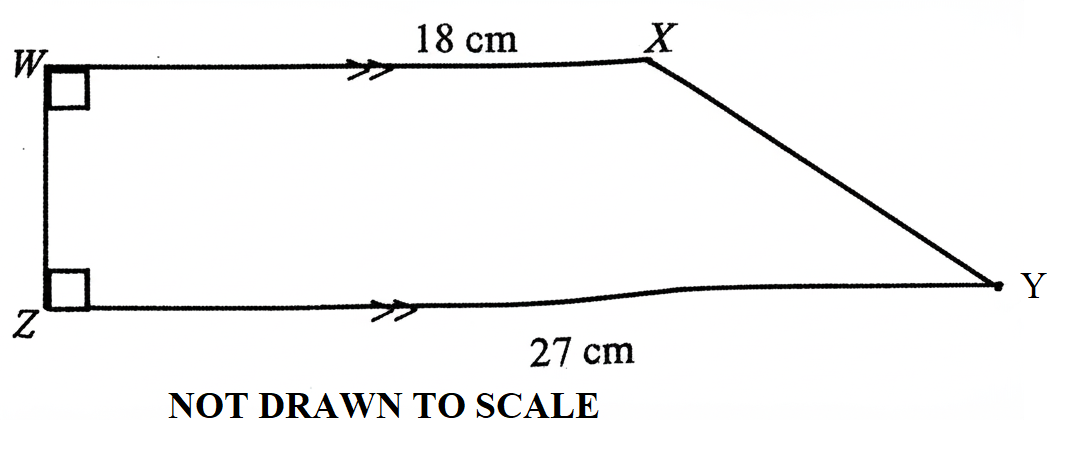
29.
In the diagram, trapezium \( WXYZ \) has \( \angle XWZ = \angle WZY = 90^\circ \). Given that \( |\overline{WX}| = 18 \) cm, \( |\overline{ZY}| = 27 \) cm, and the area is \( 270 \) cm², find the perimeter.
A. \( 72 \) cmB. \( 70 \) cmC. \( 67 \) cmD. \( 57 \) cm
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Compute the height \( WZ \) using the area formula.
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times (b_1 + b_2) \times h
\]
Substituting the given values:
\[
270 = \frac{1}{2} \times (18 + 27) \times h
\]
\[
270 = \frac{1}{2} \times 45 \times h
\]
\[
270 = 22.5 \times h
\]
\[
h = \frac{270}{22.5} = 12 \text{ cm}
\]
Step 2: Compute \( XY \) using the Pythagorean theorem.
\[
XY^2 = WX^2 + WZ^2
\]
\[
XY^2 = 18^2 + 12^2
\]
\[
XY^2 = 324 + 144
\]
\[
XY = \sqrt{468} = 15 \text{ cm}
\]
Step 3: Compute the perimeter.
\[
P = WX + XY + ZY + WZ
\]
\[
P = 18 + 15 + 27 + 12
\]
\[
P = 72 \text{ cm}
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ 72 \) cm.
30. The diameter of a sphere is 42 cm. Find the volume.
A. \( 19,404 \) cm³B. \( 25,488 \) cm³C. \( 35,544 \) cm³D. \( 38,808 \) cm³
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Use the formula for the volume of a sphere.
\[
V = \frac{4}{3} \pi r^3
\]
Step 2: Find the radius.
Since the diameter is 42 cm:
\[
r = \frac{42}{2} = 21 \text{ cm}
\]
Step 3: Substitute into the formula.
\[
V = \frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times (21)^3
\]
\[
V = \frac{4}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 9261
\]
Step 4: Simplify.
\[
\frac{4}{3} \times 9261 = \frac{37044}{3} = 12348
\]
\[
V = \frac{12348 \times 22}{7}
\]
\[
V = \frac{271656}{7} = 38,808 \text{ cm}^3
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ 38,808 \) cm³.
31. Given that \( 32 \mod 6 = P \), find the value of \( P \).
A. \( 2 \)B. \( 3 \)C. \( 4 \)D. \( 5 \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Understand modulo operation.
Modulo finds the remainder when one number is divided by another.
\[
32 \div 6 = 5 \text{ remainder } r
\]
Step 2: Calculate the remainder.
Multiplying:
\[
6 \times 5 = 30
\]
Subtracting:
\[
32 - 30 = 2
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ 2 \).
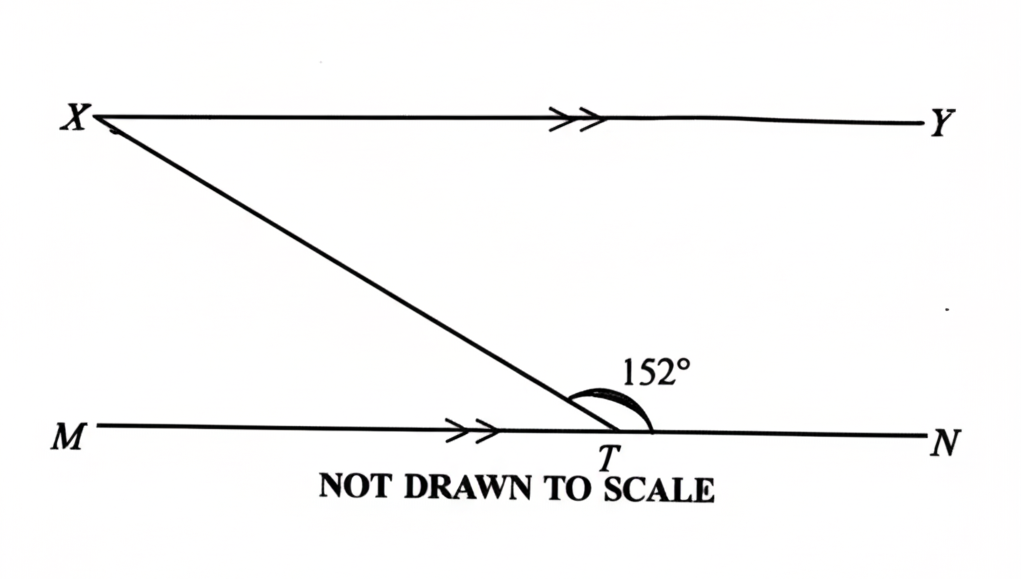
32.
In the diagram, \( \overline{XY} \parallel \overline{MN} \) and \( \angle XTN = 152^\circ \). Find \( \angle TXY \).
A. \( 152^\circ \)B. \( 54^\circ \)C. \( 36^\circ \)D. \( 28^\circ \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Use the supplementary angle rule.
Since \( \overline{XY} \parallel \overline{MN} \), angles \( XTN \) and \( TXY \) form a supplementary pair:
\[
\angle TXY = 180^\circ - \angle XTN
\]
Step 2: Substitute the given values.
\[
\angle TXY = 180^\circ - 152^\circ
\]
\[
\angle TXY = 28^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ 28^\circ \).
33. A television set was sold for Le 4,800.00 at a loss of 20%. Find the cost price.
A. Le 6,000.00B. Le 7,500.00C. Le 5,400.00D. Le 5,000.00
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Use the cost price formula.
\[
\text{Cost Price} = \frac{\text{Selling Price}}{1 - \text{Loss Percentage}}
\]
Step 2: Substitute the given values.
\[
\text{Cost Price} = \frac{4800}{1 - 0.20}
\]
\[
= \frac{4800}{0.80}
\]
Step 3: Calculate the cost price.
\[
\text{Cost Price} = 6000
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ \text{Le } 6,000.00 \).
34. An arc subtends an angle of \( 40^\circ \) at the centre of a circle of radius 21 cm. What is the area of the sector containing the angle?
A. 154 cm²B. 144 cm²C. 124 cm²D. 77 cm²
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Use the formula for the area of a sector.
\[
\text{Area of sector} = \frac{\theta}{360^\circ} \times \pi r^2
\]
Step 2: Substitute the given values.
\[
\text{Area of sector} = \frac{40}{360} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 21^2
\]
Step 3: Simplify.
\[
= \frac{1}{9} \times \frac{22}{7} \times 441
\]
\[
= \frac{22 \times 441}{63}
\]
\[
= \frac{9702}{63} = 154 \text{ cm}^2
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ 154 \) cm².
Age (years)
3
4
5
6
7
Number of Children
9
16
27
15
3
The table shows the distribution of the ages of children at a clinic on a certain day.
Use the information to answer questions 35 and 36 .
35. Calculate, correct to the
nearest whole number, the mean age of the children.
A. 4B. 5C. 6D. 7
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Multiply each age by the number of children.
\[
(3 \times 9) + (4 \times 16) + (5 \times 27) + (6 \times 15) + (7 \times 3)
\]
\[
= 27 + 64 + 135 + 90 + 21\] \[= 337
\]
Step 2: Find the total number of children.
\[
9 + 16 + 27 + 15 + 3 = 70
\]
Step 3: Calculate the mean age.
\[
\text{Mean} = \frac{337}{70} \approx 4.81 \approx 5
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ 5 \).
36. Find the median age.
A. 4B. 5C. 6D. 7
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Find the total number of children.
\[
9 + 16 + 27 + 15 + 3 = 70
\]
Step 2: Find the median position.
\[
\text{Median position} = \frac{70 + 1}{2}\] \[= 35.5^{\text{th}} \text{ position}
\]
Step 3: Use the cumulative frequency to find where the median falls.
Up to age 3: 9 children
Up to age 4: 9 + 16 = 25 children
Up to age 5: 25 + 27 = 52 children
The 35.5th child falls within the age group 5.
Final Answer: \( B.\ 5 \).
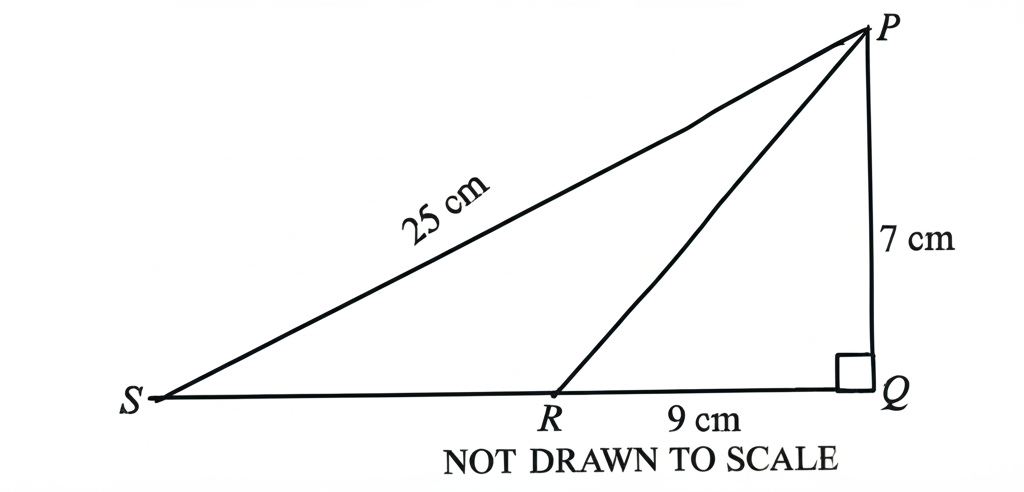
37.
In the diagram, given that \( PQ = 7 \) cm, \( RQ = 9 \) cm, and \( PS = 25 \) cm, find the length of \( SR \).
A. 9 cmB. 11 cmC. 12 cmD. 13 cm
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Apply the Pythagorean theorem to find \( PR \).
\[
PR^2 = PQ^2 + RQ^2
\]
\[
PR^2 = 7^2 + 9^2
\]
\[
PR^2 = 49 + 81
\]
\[
PR = \sqrt{130} \approx 11.4 \text{ cm}
\]
Step 2: Compute \( SR \) using \( PS = PR + SR \).
\[
SR = PS - PR
\]
\[
SR = 25 - 11.4
\]
\[
SR \approx 13.6 \text{ cm}
\]
Final Answer: \( D.\ 13 \) cm.
38. In the diagram, PYT is a circle centre O, reflex ∠POT = 216° and ∠OPY = 28°. Find the value of q.
A. 44°B. 28°C. 56°D. 108°
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: A
Step 1: Find the minor angle ∠POT.
The full angle at the center is 360°, so:
\[
\text{Minor } \angle POT\] \[= 360^\circ - 216^\circ = 144^\circ
\]
Step 2: Find ∠PYT (the angle at the circumference).
The angle at the circumference is half the angle at the center.
\[
\angle PYT = \frac{1}{2} \times 144^\circ = 72^\circ
\]
Step 3: Use the sum of angles in triangle PYT.
Given: ∠OPY = 28°
Let’s find ∠YPT:
In the isosceles triangle POT, the base angles are equal.
\[
\angle OTP = \angle OPT\] \[= \frac{180^\circ - 144^\circ}{2} = 18^\circ
\]
So, ∠YPT = 28° + 18° = 46°
Sum of angles in triangle PYT:
\[
46^\circ + 72^\circ + \angle PTY = 180^\circ
\]
\[
\angle PTY = 180^\circ - 118^\circ = 62^\circ
\]
Since ∠PTy = ∠PTO + q and ∠PTO = 18°, then:
\[
q = 62^\circ - 18^\circ = 44^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( A.\ 44^\circ \)
39. Which of the following is not a property of a rhombus?
B. All angles are acute.A. All four sides are equal.C. It has two lines of symmetry.D. Diagonals bisect at right angles.
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Reason: In a rhombus:
All four sides are equal.
It has two lines of symmetry.
Diagonals bisect each other at right angles.
Not all angles are acute. In fact, a rhombus usually has two acute angles and two obtuse angles.
Final Answer: \( B. \) All angles are acute.
40. The sum of four consecutive odd numbers is 336. Find the smallest of the numbers.
A. 79B. 81C. 89D. 91
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Let the smallest odd number be \( x \).
The next three consecutive odd numbers are \( x + 2 \), \( x + 4 \), and \( x + 6 \).
Step 2: Set up the equation.
\[
x + (x + 2) + (x + 4) + (x + 6)\] \[= 336
\]
Step 3: Simplify the equation.
\[
4x + 12 = 336
\]
\[
4x = 336 - 12
\]
\[
4x = 324
\]
\[
x = 81
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ 81 \)
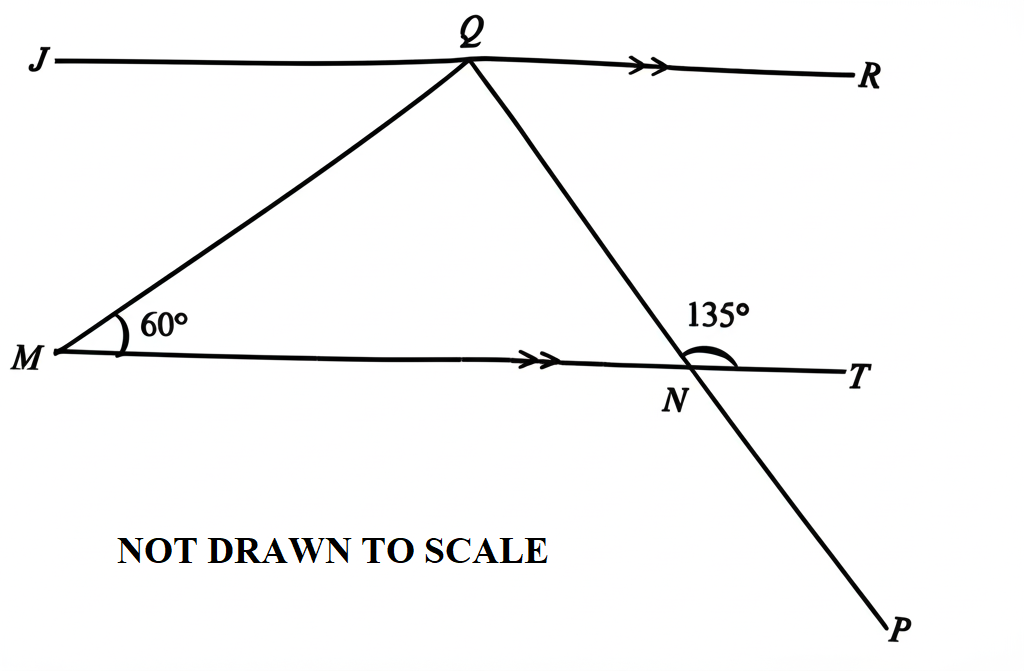
In the diagram, \( \overline{JR} \parallel \overline{MT} \), \( \angle QMT = 60^\circ \), and \( \angle QNT = 135^\circ \).
Use the information to answer questions 41 and 42 .
41. Find \( \angle RQP \).
A. 60°B. 90°C. 120°D. 135°
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Identify Given Angles:
\( \angle QMT = 60^\circ \)
\( \angle QNT = 135^\circ \)
\( JR \parallel MT \) (meaning corresponding and alternate angles apply)
Step 2: Find \( \angle MQN \)
Since \( QMT \) and \( QNT \) form a straight line, their sum is \( 180^\circ \):
\[
\angle MQN = 180^\circ - \angle QMT\] \[= 180^\circ - 60^\circ = 120^\circ
\]
Step 3: Find \( \angle RQP \)
Since \( JR \parallel MT \), \( \angle MQN \) is an alternate angle to \( \angle RQP \).
So, \( \angle RQP = 120^\circ \)
Final Answer: \( C.\ 120^\circ \)
42. Find \( \angle MQP \).
A. 75°B. 60°C. 135°D. 55°
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Identify Given Angles:
\( \angle QMT = 60^\circ \)
\( \angle QNT = 135^\circ \)
Since \( \angle QMT \) and \( \angle QNT \) form a straight line:
\[
\angle MQN = 180^\circ - \angle QMT\] \[= 180^\circ - 60^\circ = 120^\circ
\]
Step 2: Find \( \angle MQP \) Using Alternate Angles:
Since \( JR \parallel MT \), \( \angle MQN \) is alternate to \( \angle MQP \):
\[
\angle MQP = \angle QMT = 60^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ 60^\circ \)
43. The probability that two pupils pass an examination are 25% and 60%. Find the probability that the two pupils fail the examination.
A. \( \frac{1}{10} \)B. \( \frac{3}{10} \)C. \( \frac{3}{20} \)D. \( \frac{1}{20} \)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Calculate the probability of each pupil failing.
Probability that the first pupil fails: \( 1 - 0.25 = 0.75 \)
Probability that the second pupil fails: \( 1 - 0.60 = 0.40 \)
Step 2: Multiply the probabilities since the events are independent.
\[
P(\text{both fail}) = 0.75 \times 0.40\] \[= 0.30 = \frac{3}{10}
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ \frac{3}{10} \)
44. Factorize completely: \( 5k^2 - 15pk + 6k - 18p \)
A. \((k + 3p)(5k + 6)\)B. \((k - 3p)(5k + 6)\)C. \((k - 3p)(5k - 6)\)D. \((k + 3p)(5k - 6)\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Group the terms:
\[
5k^2 - 15pk + 6k - 18p\] \[= (5k^2 - 15pk) + (6k - 18p)
\]
Step 2: Factor out common terms in each group:
\[
= 5k(k - 3p) + 6(k - 3p)
\]
Step 3: Factor out the common binomial factor:
\[
= (k - 3p)(5k + 6)
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ (k - 3p)(5k + 6) \)
45. A bag contains 6 red, 4 yellow and 2 blue balls all of the same size and weight. If a ball is picked at random from the bag, find the probability that the ball is red or blue.
A. \(\frac{1}{5}\)B. \(\frac{2}{5}\)C. \(\frac{1}{3}\)D. \(\frac{2}{3}\)
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Total number of balls = 6 (red) + 4 (yellow) + 2 (blue) = 12
Number of favorable outcomes (red or blue) = 6 + 2 = 8
So, the probability of picking a red or blue ball is:
\[
P(\text{red or blue}) = \frac{8}{12} = \frac{2}{3}
\]
Final Answer: D
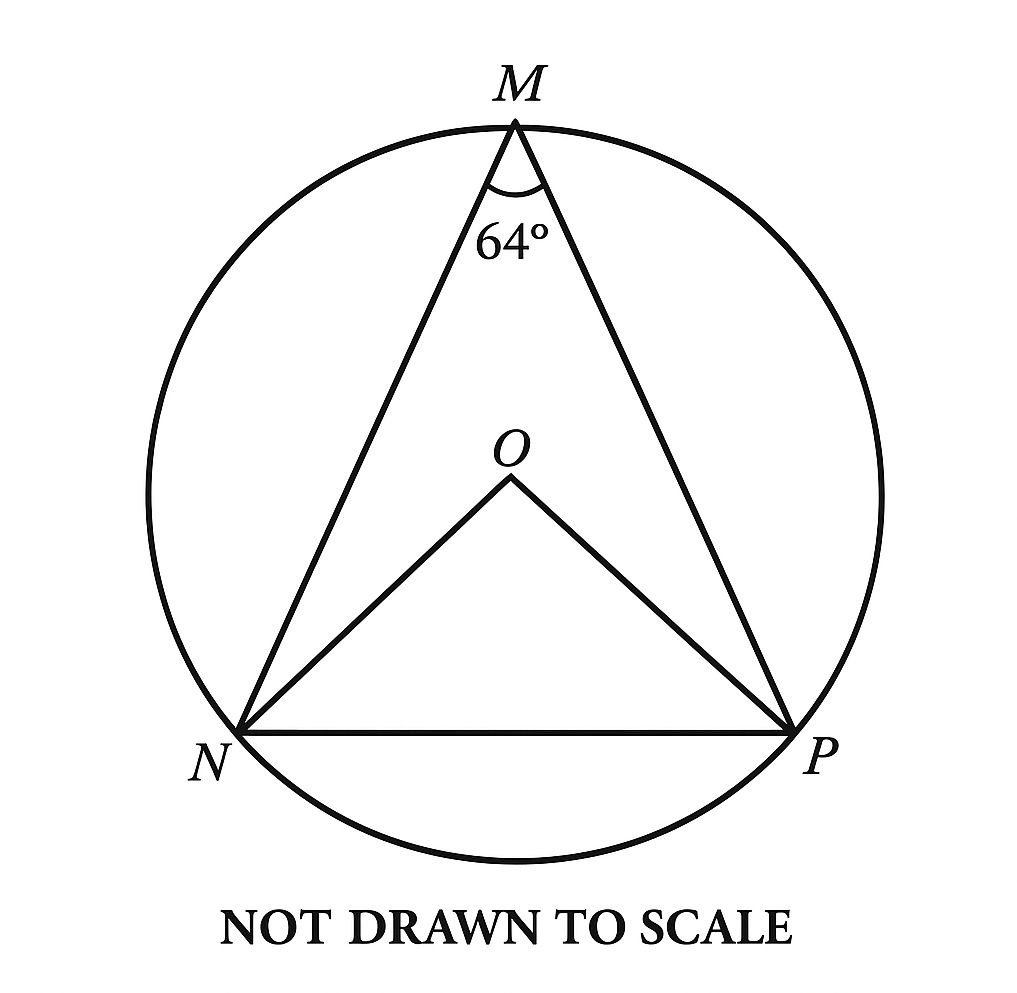
46.
In the diagram M, N and P are points on a circle centre O. If ∠NMP = 64°, find ∠ONP.
A. 64°B. 26°C. 32°D. 52°
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: B
Step 1: Identify Key Relationships.
Points M, N, and P lie on a circle centered at O.
∠NMP = 64° is an inscribed angle subtending arc NP.
The central angle ∠NOP subtending the same arc is twice the inscribed angle.
Step 2: Compute ∠NOP.
\[
\angle NOP = 2 \times \angle NMP\] \[= 2 \times 64^\circ = 128^\circ
\]
Step 3: Consider Triangle NOP.
ON = OP because they are radii, so △NOP is isosceles.
Let the base angles be x. By the sum of angles in a triangle:
\[
x + x + 128^\circ = 180^\circ
\]
\[
2x = 52^\circ \quad \Rightarrow \quad x = 26^\circ
\]
Final Answer: \( B.\ 26^\circ \)
47. The heights, in cm, of 5 mango seedlings are 1, 3, 4, 5, and 7. Calculate the mean deviation.
A. 1.2B. 1.4C. 1.6D. 1.8
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Find the mean.
\[
\text{Mean} = \frac{1 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 7}{5}\] \[= \frac{20}{5} = 4
\]
Step 2: Find the absolute deviations.
|1 - 4| = 3
|3 - 4| = 1
|4 - 4| = 0
|5 - 4| = 1
|7 - 4| = 3
Step 3: Calculate the mean deviation.
\[
\text{MD} = \frac{3 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 3}{5}\] \[= \frac{8}{5} = 1.6
\]
Final Answer: \( C.\ 1.6 \)
48. The sum of four consecutive even numbers is 252. Find the difference between the largest and the smallest number.
A. 2B. 4C. 6D. 8
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: C
Step 1: Let the four consecutive even numbers be \( x \), \( x + 2 \), \( x + 4 \), and \( x + 6 \).
Step 2: Set up the equation:
\[
x + (x + 2) + (x + 4) + (x + 6)\] \[= 252
\]
Step 3: Simplify:
\[
4x + 12 = 252
\]
\[
4x = 240 \quad \Rightarrow \quad x = 60
\]
Step 4: The smallest number is 60, the largest is 60 + 6 = 66.
Difference:
\[
66 - 60 = 6
\]
Final Answer: C. 6
49. A line passes through the point (2, −4). If the gradient of the line is \( \frac{1}{2} \), find the equation of the line.
A. x + 2y = 10B. x − 2y = 10C. 2x + y = 10D. 2x − y = 10
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Use the point-slope form of a straight line:
\[
y - y_1 = m(x - x_1)
\]
Given: Gradient \( m = \frac{1}{2} \) and point \( (2, -4) \).
Step 2: Substitute values:
\[
y - (-4) = \frac{1}{2}(x - 2)
\]
\[
y + 4 = \frac{1}{2}x - 1
\]
Step 3: Multiply through by 2 to clear the fraction:
\[
2y + 8 = x - 2
\]
Step 4: Rearrange:
\[
x - 2y = 10
\]
Final Answer: D. 2x − y = 10
50. For what value of \( x \) is \( \frac{x^2 + 15x + 50}{x - 5} \) not defined?
A. −10B. −5C. 10D. 5
See Explanation
Explanation:
The correct answer is: D
Step 1: Identify the restriction.
The fraction is not defined when the denominator is zero.
\[
x - 5 = 0
\]
Step 2: Solve for \( x \).
\[
x = 5
\]
Conclusion: The expression is not defined when \( x = 5 \).
Final Answer: D. 5
END OF PAPER
Back