

SECTION A
[50 marks]
Answer all the questions in this section.
1. The illustration below is an incomplete diagram of an organism. Study it and answer questions 1(a) to 1(e).
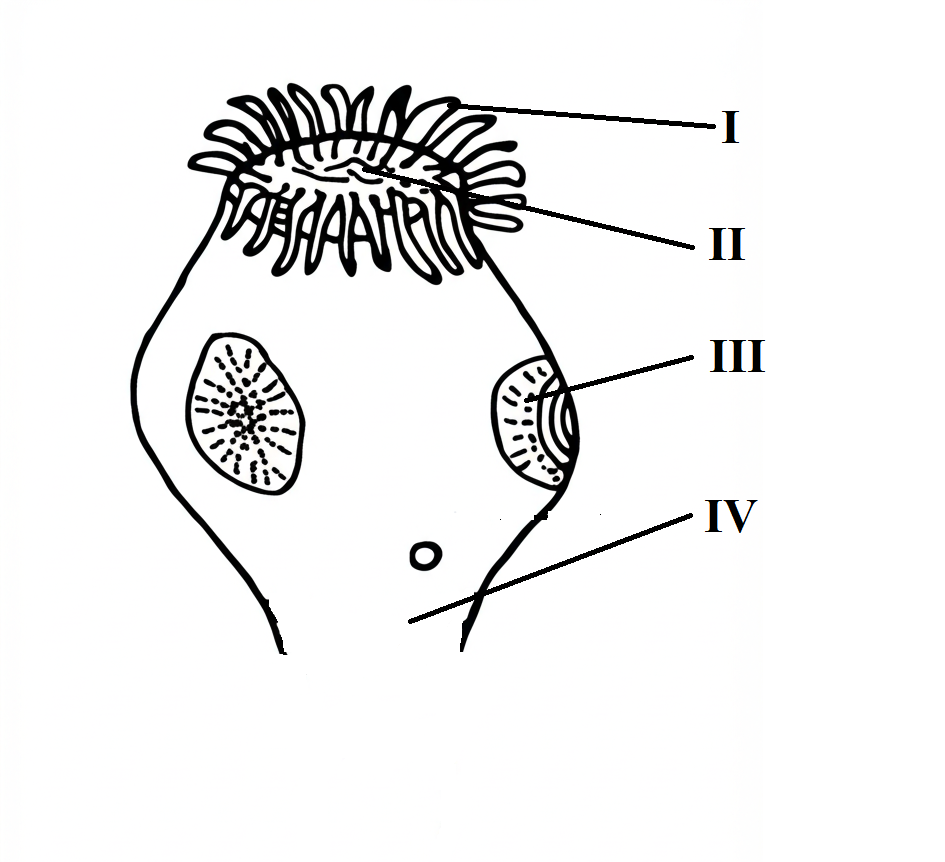
(a) (i) Identify the organism illustrated.
[1 mark]
(ii) Name the parts labelled I to IV.
I:_________
II:_________
III:_________
IV:_________
[2 marks]
(iii) State one function each of the parts labelled I, III and IV.
I:_________
III:_________
IV:_________
[3 marks]
(b) Name the habitat, Phylum, feeding habit, body symmetry and type of reproduction of the illustrated organism.
Habitat:_________
Phylum:_________
Feeding habit:_________
Body symmetry:_________
Type of reproduction:_________
[5 marks]
(c) State two adaptations of the illustrated organism to its mode of feeding.
_________
_________
[4 marks]
(d) On the diagram, complete the drawing of the illustrated organism and label fully.
[5 marks]
(e) (i) Name three animals that have the same feeding habit as the illustrated organism.
_________
_________
_________
[3 marks]
(ii) Name two plants that have the same feeding habit as the illustrated organism.
_________
_________
[2 marks]
Answers to Questions 1a - e(ii)
(1)(a) (i) The organism illustrated is
Planaria/Tapeworm/Liver fluke
(ii) The parts labelled I to IV are:
I: Sucker/Rostellum with hooks
II: Scolex/Head
III: Eye spot/Auricle
IV: Body/Trunk/Neck
(iii) The functions of the parts labelled I, III and IV are:
I: For attachment
III: Sensory reception/ photoreception
IV: Contains reproductive organs and other body systems
(b) The habitat, Phylum, feeding habit, body symmetry and type of reproduction:
Habitat: Freshwater/Intestine of vertebrates/Liver of vertebrates
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Feeding habit: Parasitic/Free-living carnivorous
Body symmetry: Bilateral
Type of reproduction: Sexual/Asexual
(c) Two adaptations of the illustrated organism to its mode of feeding:
- Presence of suckers/hooks for attachment to the host.
- Absence of a well-developed digestive system.
- Ability to absorb digested food directly from the host.
- Production of a large number of eggs to increase chances of survival.
(d) Complete Diagram
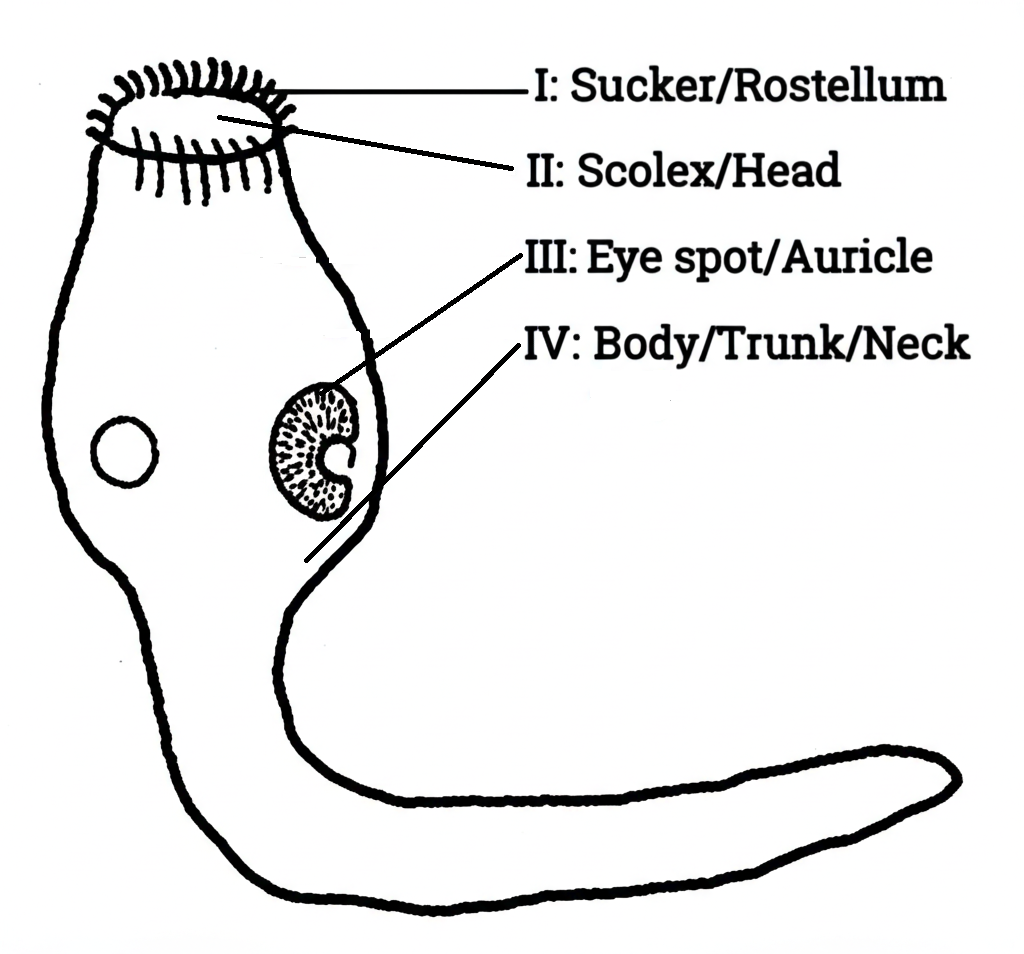
(e) (i) Three animals that have the same feeding habit:
Hookworm,
Roundworm,
Ascaris
(ii) Two plants that have the same feeding habit:
Dodder (Cuscuta),
Mistletoe
2. The diagram below is an illustration of the life cycle of an organism. Study it and answer questions 2(a) to 2(f).
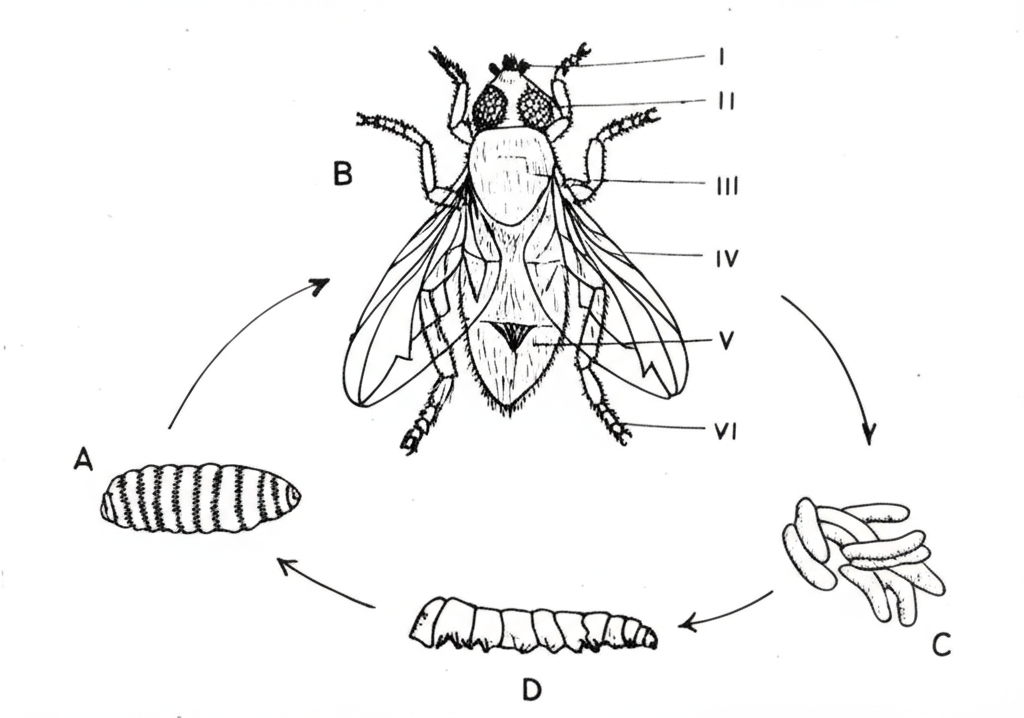
(a) (i) Name the organism that possesses the life cycle illustrated.
________________________
[1 mark]
(ii) Name the type of metamorphosis in the life cycle illustrated.
________________________
[1 mark]
(b) State the Phylum and Class of the organism illustrated.
(i) Phylum:________________
(ii) Class: _________________
[2 marks]
(c) (i) Give three reasons for the answers in 2(b).
________________________
________________________
________________________
[3 marks]
(ii) Give two examples of organisms that belong to the Class named in 2(b)(ii).
________________________
________________________
[2 marks]
(iii) Name two other Classes of the Phylum stated in 2(b)(i).
________________________
________________________
[2 marks]
(d) (i) Name the stages labelled A, B, C and D.
A: _________________
B: _________________
C: _________________
D: _________________
[4 marks]
(ii) State one way each by which the stages labelled B and D are of economic importance.
B: _________________
D: _________________
[2 marks]
(iii) What is the common name for the stage labelled D?
D: _________________
[1 mark]
(e) Identify the parts labelled I to VI.
I: _________________
II: _________________
III: _________________
IV: _________________
V: _________________
VI: _________________
[3 marks]
(f) Which of the illustrated stages:
(i) is dormant; _______________
(ii) attaches to the surface; ____________
(iii) lives on decomposing matter; __________
(iv) is a fluid feeder? _____________
[4 marks]
Answers to Questions 2a - f (iv)
(2)(a) (i) The organism that possesses the life cycle illustrated is Housefly
(ii) The type of metamorphosis in the life cycle illustrated is Complete metamorphosis
(b) The Phylum and Class of the organism illustrated.
(i) Phylum: Arthropoda
(ii) Class: Insecta
(c) (i) Three reasons for the answers in 2(b) are:
- The adult organism (B) has three distinct body segments: head, thorax, and abdomen.
- The adult organism (B) possesses three pairs of legs attached to the thorax.
- The adult organism (B) has a pair of wings (IV) attached to the thorax.
(ii) Two examples of organisms that belong to the Class Insecta are Mosquitoes, Butterflies
(iii) Two other Classes of the Phylum Arthropoda are Crustacea, Arachnida
(d) (i) Name the stages labelled A, B, C and D.
A: Pupa
B: Adult (Housefly)
C: Eggs
D: Larva (Maggot)
(ii) State one way each by which the stages labelled B and D are of economic importance.
B: Adult houseflies can act as pollinators for some plants, although they are mostly known for transmitting diseases.
D: Fly larvae (maggots) can be used in forensic entomology to estimate the time of death and can also be used in maggot debridement therapy to clean wounds.
(iii) What is the common name for the stage labelled D?
D: Maggot
(e) Identify the parts labelled I to VI.
I: Antenna
II: Compound Eye
III: Thorax
IV: Wing
V: Abdomen
VI: Leg
(f) Which of the illustrated stages:
(i) is dormant; A (Pupa)
(ii) attaches to the surface; A (Pupa)
(iii) lives on decomposing matter; D (Larva/Maggot)
(iv) is a fluid feeder? B (Adult Housefly)
SECTION B
[30 marks]
Answer all the questions in this section.
3. The diagrams below are illustrations of fruits. A, B and C are sections of the fruits. Study them and answer questions 3(a) to 3(e).
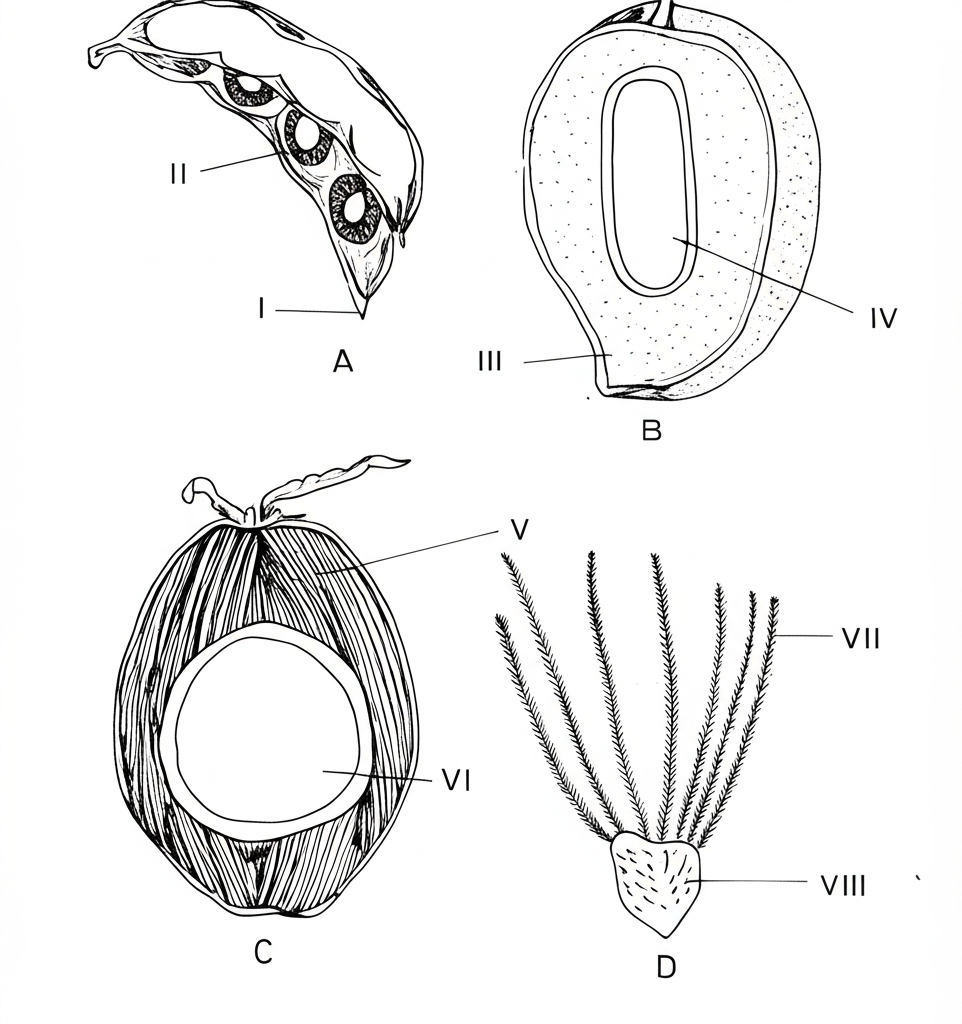
(a) Name the parts labelled I to VIII.
I: _________________________
II: _________________________
III: _________________________
IV: _________________________
V: _________________________
VI: _________________________
VII: _________________________
VIII: _________________________
[4 marks]
(b) Complete the table below
| Fruits | Name of fruit | Mode of dispersal of fruit |
|---|---|---|
| A | ||
| B | ||
| C | ||
| D |
[8 marks]
(c) State one structural adaptation each of the fruits illustrated in diagrams A, B, C and D to their modes of dispersal.
A: ________________________
B: ________________________
C: ________________________
D: ________________________
[8 marks]
(d) Name the types of placentation in fruits A, B and C.
A: _______________________
B: _______________________
C: _______________________
[3 marks]
(e) Name one of the illustrated fruits that is a:
(i) simple fruit; ____________
(ii) drupe; __________________
(iii) dehiscent fruit; _________
(iv) false fruit; _____________
(v) succulent fruit; _________
(vi) cypsela; ________________
(vii) legume. ________________
[7 marks]
Answers to Questions 3a - e
(3)(a) Name the parts labelled I to VIII.
I: Pericarp/Pod Wall
II: Seed
III: Mesocarp
IV: Endocarp
V: Fibrous Mesocarp
VI: Endosperm/Kernel
VII: Pappus/Hairs
VIII: Achene
(b) Complete the table below
| Fruits | Name of fruit | Mode of dispersal of fruit |
|---|---|---|
| A | Bean | Explosion/Mechanical |
| B | Mango/Peach/Olive/Drupe | Animal (Ingestion) |
| C | Coconut | Water |
| D | Dandelion fruit | Wind |
(c) State one structural adaptation each of the fruits illustrated in diagrams A, B, C and D to their modes of dispersal.
A: Has a pod that dries and splits open explosively, scattering the seeds.
B: Has a fleshy mesocarp that is attractive to animals for ingestion.
C: Has a fibrous mesocarp that makes it buoyant, allowing dispersal by water.
D: Possesses a pappus of light, hair-like structures that increase surface area for wind dispersal.
(d) Name the types of placentation in fruits A, B and C.
A: Marginal
B: Basal
C: Basal
(e) One of the illustrated fruits that is a:
(i) simple fruit; A (Bean), B (Mango), C (Coconut)
(ii) drupe; B (Mango)
(iii) dehiscent fruit; A (Bean)
(iv) false fruit; None of the illustrated fruits are typically classified as false fruits.
(v) succulent fruit; B (Mango)
(vi) cypsela; D (Dandelion fruit - the achene is the actual fruit)
(vii) legume. A (Bean)